The Japan-led XRISM (X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission) observatory has released an initial check out the extraordinary information it will accumulate when scientific research procedures start later this year.
The satellite’s scientific research group launched a picture of a cluster of numerous galaxies and a spectrum of stellar wreckage in a neighboring galaxy, which gives scientists a thorough check out its chemical makeup.
“XRISM will supply the global science area with a new glimpse of the concealed X-ray skies,” claimed Richard Kelley, the united state principal investigator for XRISM at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Facility in Greenbelt, Maryland. “We’ll not only see X-ray images of these resources, but also study their make-ups, motions, and physical states.”
The X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM), articulated “crism,” is spearheaded by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency(JAXA) in partnership with the National Aeronautics and Area Management (NASA) and the European Space Firm (ESA). It began its journey on September 6, 2023.
This device is capable of noticing X-rays with energies varying aproximately 12,000 times that of visible light, and it will check out the cosmos’ most extreme environments, including the best areas, vastest frameworks, and things with the most extreme gravitational pull.
The mission has two tools, Settle and Xtend, each at the focus of an X-ray Mirror Assembly created and built at Goddard.
Fix is a spectrometer that makes use of a microcalorimeter and was produced collectively by NASA and JAXA. It functions within a container of liquid helium that has to do with the exact same size as a fridge and maintains a temperature just somewhat over absolute zero.
Deal with’s 6-by-6-pixel detector experiences a rise in temperature when it is subjected to an X-ray. This temperature level adjustment is directly symmetrical to the energy of the X-ray. By examining the power of each X-ray, the tool has the ability to give brand-new understandings into the source of the X-rays.
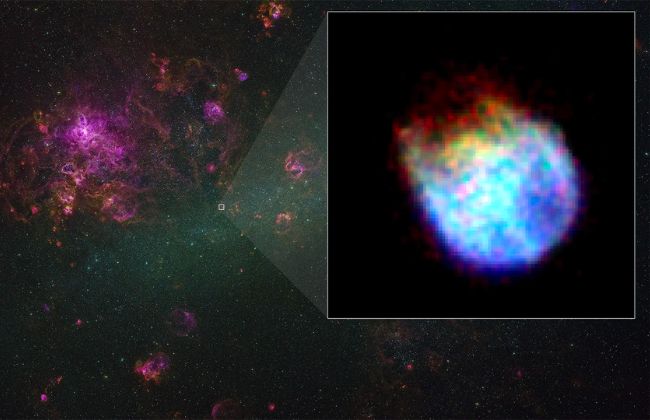
The goal group used Resolve to examine N132D, a supernova residue and one of the brightest X-ray sources in the Huge Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy around 160,000 light-years away in the southern constellation Dorado. The increasing wreck is approximated to be regarding 3,000 years old and was created when a celebrity about 15 times the Sun’s mass ran out of fuel, collapsed, and exploded.
The Willpower range shows tops related to silicon, sulfur, calcium, argon, and iron. This is the most thorough X-ray spectrum of the item ever obtained and shows the incredible science the goal will certainly do when normal procedures start later in 2024.

Credit: JAXA/NASA/XRISM Xtend; background, DSS
“These aspects were built in the initial celebrity and then blew up away when it blew up as a supernova,” claimed Brian Williams, NASA’s XRISM job scientist at Goddard. “Resolve will allow us to see the forms of these lines in a way never possible before, allowing us figure out not just the abundances of the various elements present, yet also their temperatures, densities, and instructions of activity at extraordinary levels of accuracy. From there, we can assemble details about the initial celebrity and the surge.”
XRISM’s 2nd instrument, Xtend, is an X-ray imager developed by JAXA. It offers XRISM a big field of vision, allowing it to observe a location about 60% larger than the ordinary evident dimension of the moon.
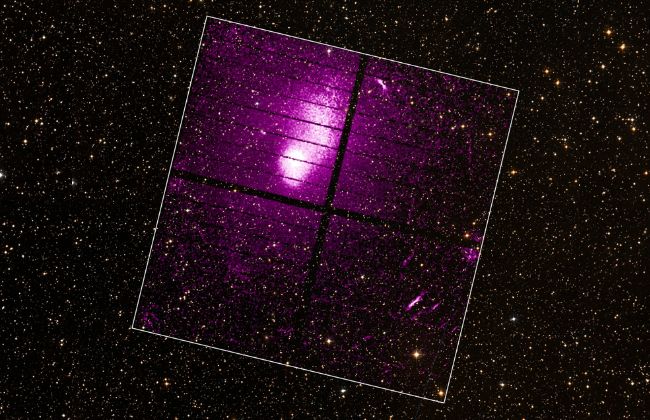
Xtend captured an X-ray image of Abell 2319, a rich galaxy collection regarding 770 million light-years away in the north constellation Cygnus. It’s the 5th brightest X-ray cluster overhead and is currently undertaking a significant merger event.
Xtend’s extensive field of view is showcased by the massive cluster, which spans an excellent 3 million light-years across.
“The XRISM job at Goddard is enjoyed see Resolve exceeding our expectations even prior to the appointing process is complete,” remarks Lillian Reichenthal, NASA’s task manager. “Our first goal was to achieve a spectral resolution of 7 electron volts, however with the tool currently in orbit, we’re in fact achieving 5. This suggests we’ll acquire even more in-depth chemical maps from each range caught by XRISM, exceeding our original goals.”
Deal with is executing remarkably and already conducting amazing scientific research regardless of a problem with the aperture door covering its detector. The door, created to secure the detector before launch, has closed as planned after several efforts. The door blocks lower-energy X-rays, effectively reducing the objective off at 1,700 electron volts contrasted to the intended 300. The XRISM team will remain to discover the anomaly and is examining different strategies to opening the door. The Xtend tool is unaffected.
NASA’s XRISM General Viewer Center, hosted at Goddard, is accepting proposals for monitorings from members of U.S. and Canadian organizations via Thursday, April 4. Cycle 1 of XRISM General Observer examinations will start in the summer of 2024.
XRISM is a joint goal in between JAXA and NASA, with involvement by ESA. NASA’s contribution consists of science involvement from the Canadian Room Firm.